In the recent national finals of the 6th DIGIX Global AI Challenge, contestants have competed in 18 subdivisions, including AI plus Four New Disciplines, AI plus Future Scenarios, Steel Surface Defect Detection and Segmentation, AI-Generated Facial Image Identification, Autonomous Vehicle Visual Navigation Challenge, and Autonomous Vehicle Task Challenge.

The School of Software Engineering (SSE) creates new highlights in the competition by clinching 3 national first prizes, 2 national second prizes and 1 national third prize.
National First Prize
Algorism Innovation: AI plus New Agricultural Science
Project: Stomatal phenotyping measurement model based on a multi-task UR-CNN algorithm
Mentor: Huang Xiaotao
Members: Cao Qi, Yang Jinjiao, Cheng Jiayi
Overview:
As plant phenomics and smart agriculture continue to advance, high-throughput phenotyping extraction has become a major area of research interest. Stomata, critical channels for gas exchange between plants and the external environment, significantly influence plant growth owing to their density and distribution. However, traditional manual counting methods are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to subjective errors. To address these limitations, this study proposes a stomatal phenotyping measurement model based on a multi-task UR-CNN algorithm.
The model employs ResNet34 to extract features from plant microscopic images, with feature maps shared with both the stomatal detection subnetwork (object detection) and the cell segmentation subnetwork (semantic segmentation). The object detection branch adopts a two-stage region proposal network (RPN), where candidate bounding boxes are generated on the feature maps for classification and regression. The final stomatal count is calculated using a non-maximum suppression (NMS) algorithm. In the semantic segmentation branch, a residual convolution-based U-shaped network is constructed to generate feature probability maps consistent with the original image resolution. Cell counts are then derived via connected-domain labeling principles. Experimental results demonstrate that the model outperforms single-task models in both stomatal detection and cell segmentation accuracy, while exhibiting robust transferability and generalization across diverse datasets.

Algorism Challenge:
Project: LSB-Efficientnet-based detection of AI-generated facial images
Mentor: Wu Tao
Members: Xie Weihao, Wan Changlin, Zhao Enyue (School of Economics)
Overview:
AI-generated facial images primarily rely on deep learning technologies, particularly generative adversarial networks (GANs), variational autoencoders (VAEs), and diffusion models. These models learn the distributional patterns of real facial images and synthesize novel images with statistically similar features. This project combines deep learning and image processing techniques to detect discrepancies between authentic and AI-generated facial images, enabling high-precision identification. Through visual inspection of details and properties, the methodology can distinguish AI-generated images from authentic ones.
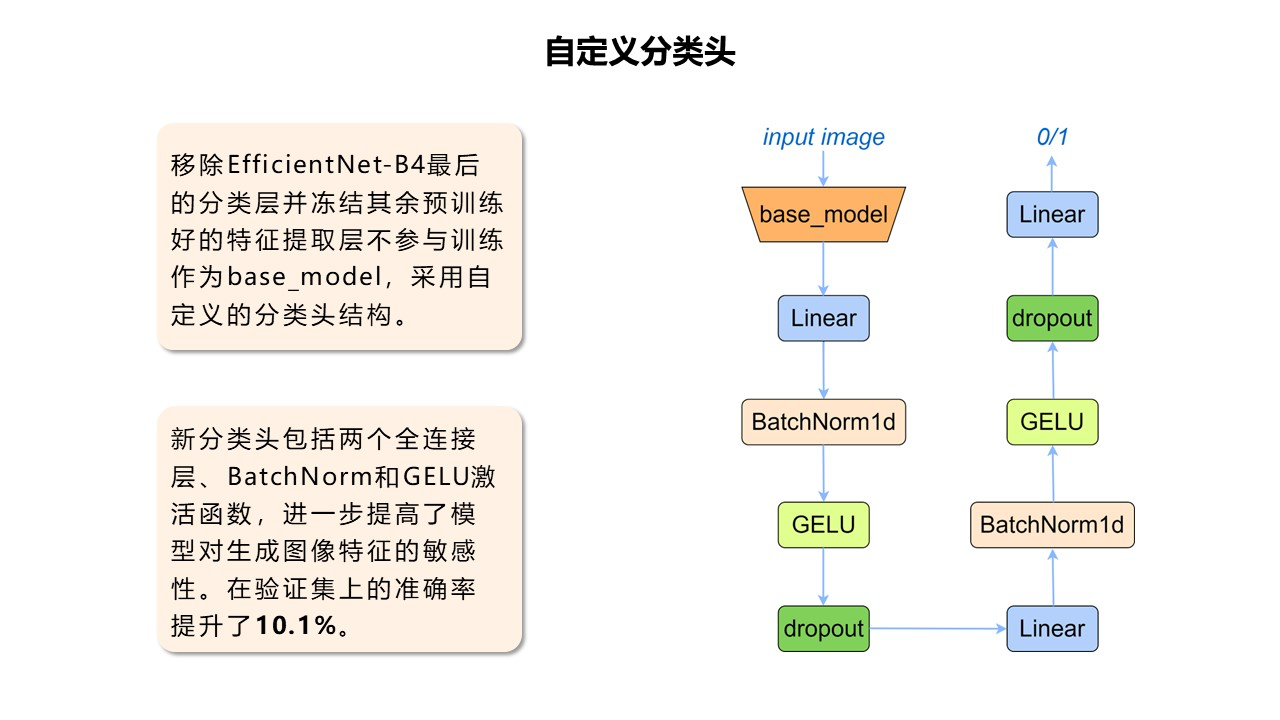

Algorism Challenge:
Project: Ultrasound image identification model based on ConvNeXt and Densenet
Members: Wang Mingjia (School of Computer Science & Technology), Yang Mingxin, Zhao Zonglin (School of Computer Science & Technology)
Overview:
Breast cancer ultrasound image classification and feature recognition face multiple challenges, including variable image quality, anatomical complexity, tumor size/shape heterogeneity, malignant-benign similarity, and data imbalance. To address these issues, we developed the MyConvNeXt model based on ConvNeXt for BIRADS six-class classification, and the MyDenseNet model based on DenseNet for feature-based binary classification by integrating channel-spatial attention mechanisms.
In data processing, multiple data augmentation techniques were employed alongside CutMix and the self-proposed CutBlack algorithm to extract image foreground content, mitigate noise interference, and enhance model accuracy and robustness. The proposed approach achieved exceptional performance in breast image classification and feature recognition tasks.
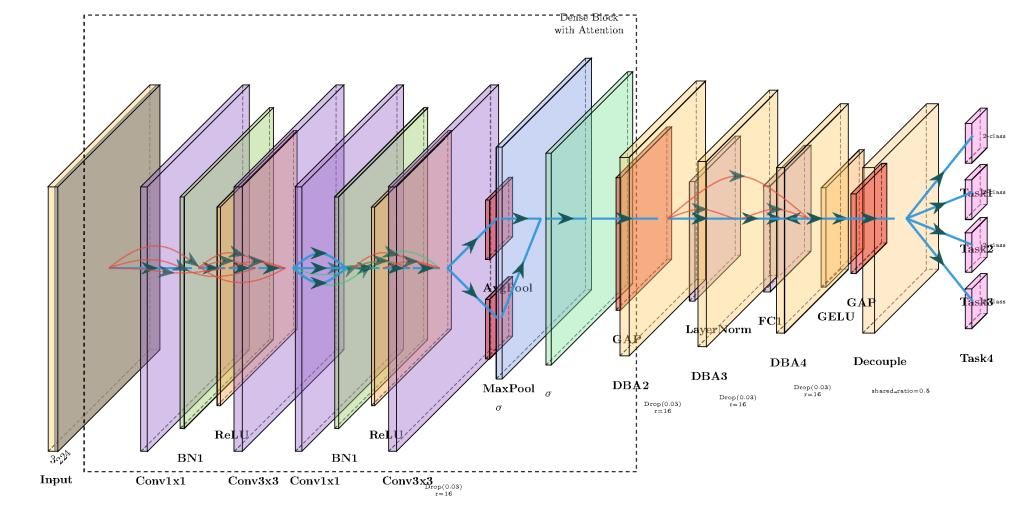
National Second Prize
Algorism Innovation: AI plus New Medicine
Project: Omnimedical
Mentor: Lu Yongzhong
Members: Xu Shengjie, Dai Rujie, Wang Weiwei
Algorism Challenge: Steel Surface Defect Detection and Segmentation
Project: Improved segformer for steel defect segmentation
Mentor: Lv Zehua, Tang He
Members: Huang Jianuo, Fan Pengcheng, Kang Chenyi
National Third Prize
Algorism Innovation: AI plus New Liberal Arts
Project: AI-driven legal assistance system
Mentor: Wu Tao, Chen Wei
Members: Nie Anqi, Zhu Shuyao (School of Mechanical Science and Engineering), Li Zhipeng
The DIGIX Global AI Challenge, an international contest for full-time undergraduate and graduate students worldwide, has been held six times. To date, it has attracted contestants from over 1,000 universities across 26 countries and regions, totaling over 37,000 students from 24,000 teams.
This year’s contest, launched in May, reaches new heights in participation, with 8,027 teams from 606 global institutions spanning China, Russia, the UK, Australia, and other countries.

Committed to producing multidisciplinary and innovative talents, SSE has encouraged students to take part in various disciplinary contests to hone their skills.

